South Island
| Sobriquet: The Mainland | |
|---|---|
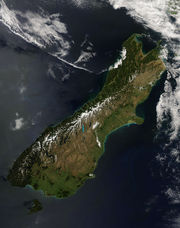 Satellite view of the South Island |
|
 South Island (New Zealand)
|
|
| Geography | |
| Location | Oceania |
| Archipelago | New Zealand |
| Area | 151,215 km2 (58,384.4 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 12th |
| Highest elevation | 3,754 m (12,316 ft) |
| Highest point | Aoraki/Mount Cook |
| Country | |
|
New Zealand
|
|
| Regions | Canterbury Marlborough Nelson Otago Southland Tasman West Coast |
| Largest city | Christchurch (pop. 390,300) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 1,038,300 (as of June 2010 estimate) |
| Density | 6.9 /km2 (17.9 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | European, Māori, Chinese |
The South Island (Māori: Te Wai Pounamu) is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand, the other being the more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean. The territory of the South Island covers 151,215 square kilometres (58,384 sq mi) and is influenced by a temperate climate.
The South Island is sometimes called the "mainland". While it has a 33% larger landmass than the North Island, only 24% of New Zealand's 4.4 million inhabitants live in the South Island. In the early stages of European (Pākehā) settlement of the country, the South Island had the majority of the European population and wealth due to the 1860s gold rushes. The North Island population overtook the South in the early 20th century, with 56% of the population living in the North in 1911, and the drift north of people and businesses continued throughout the century.[1]
History
Early inhabitants of the South Island were the Waitaha. They were largely absorbed via marriage and conquest by the Kāti Mamoe in the 16th century.
Ngāti Mamoe were in turn largely absorbed via marriage and conquest by the Ngāi Tahu who migrated south in the 17th century.[2] While today there is no distinct Ngati Mamoe organisation, many Ngai Tahu have Ngati Mamoe links in their whakapapa and, especially in the far south of the island.
Around the same time a group of Māori migrated to Rekohu (the Chatham Islands), where, by adapting to the local climate and the availability of resources, they developed a culture known as Moriori — related to but distinct from Māori culture in mainland New Zealand. A notable feature of the Moriori culture, an emphasis on pacifism, proved disadvantageous when Māori warriors arrived in the 1830s aboard a chartered European ship.[3]
The first Europeans known to reach the South Island were the crew of Dutch explorer Abel Tasman who arrived in his ships Heemskerck and Zeehaen. Tasman anchored in Golden Bay, at the northern end of the island, (he named it Murderers Bay) in December 1642 and sailed northward to Tonga following a clash with local Māori. Tasman sketched sections of the two main islands' west coasts. Tasman called them Staten Landt, after the States-General of the Netherlands, and that name appeared on his first maps of the country. Dutch cartographers changed the name to Nova Zeelandia in Latin, from Nieuw Zeeland, after the Dutch province of Zeeland. It was subsequently Anglicised as New Zealand by British naval captain James Cook of HM Bark Endeavour who visited the islands more than 100 years after Tasman during (1769–1770).

In the early 18th century, Ngāi Tahu a Māori tribe who originated on the east coast of the North Island began migrating to the northern part of the South Island. There they and Kāti Mamoe fought Ngāi Tara and Rangitāne in the Wairau Valley. Ngāti Māmoe then ceded the east coast regions north of the Clarence River to Ngāi Tahu. Ngāi Tahu continued to push south, conquering Kaikoura. By the 1730s, Ngāi Tahu had settled in Canterbury, including Banks Peninsula. From there they spread further south and into the West Coast.[4]
In 1827-1828 Ngāti Toa under the leadership of Te Rauparaha successfully attacked Ngāi Tahu at Kaikoura. Ngāti Toa then visited Kaiapoi, ostensibly to trade. When they attacked their hosts, the well-prepared Ngāi Tahu killed all the leading Ngāti Toa chiefs except Te Rauparaha. Te Rauparaha returned to his Kapiti Island stronghold. In November 1830 Te Rauparaha persuaded Captain John Stewart of the brig Elizabeth to carry him and his warriors in secret to Akaroa, where by subterfuge they captured the leading Ngāi Tahu chief, Te Maiharanui, and his wife and daughter. After destroying Te Maiharanui's village they took their captives to Kapiti and killed them. John Stewart, though arrested and sent to trial in Sydney as an accomplice to murder, nevertheless escaped conviction.[4]
In the summer of 1831–1832 Te Rauparaha attacked the Kaiapoi pā (fortified village). After a three-month siege, a fire in the pā allowed Ngāti Toa to overcome it. They then attacked Ngāi Tahu on Banks Peninsula and took the pā at Onawe. In 1832-33 Ngāi Tahu retaliated under the leadership of Tuhawaiki and others, attacking Ngāti Toa at Lake Grassmere. Ngāi Tahu prevailed, and killed many Ngāti Toa, although Te Rauparaha again escaped. Fighting continued for a year or so, with Ngāi Tahu maintaining the upper hand. Ngāti Toa never again made a major incursion into Ngāi Tahu territory.[4]
By 1839 Ngāi Tahu and Ngāti Toa established peace and Te Rauparaha released the Ngāi Tahu captives he held. Formal marriages between the leading families in the two tribes sealed the peace.
When Britain annexed New Zealand in 1840, the South Island briefly became a part of New South Wales.[5] This annexation was in response to New Zealand Company attempts to establish a separate colony in Wellington, and so Lieutenant-Governor William Hobson declared British sovereignty over all of New Zealand on 21 May 1840 (the North Island by treaty and the South by discovery).)[6]
On 17 June 1843, Māori natives and the British settlers clashed at Wairau in what became known as the Wairau Affray. Also known as the Wairau Massacre in most older texts, it was the first serious clash of arms between the two parties after the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi and the only one to take place in the South Island. Four Māori died and three were wounded in the incident, while among the Europeans the toll was 22 dead and five wounded. Twelve of the Europeans were shot dead or clubbed to death after surrendering to Māori who were pursuing them.[7]
In the 1860s, several thousand Chinese men, mostly from the Guangdong province, migrated to New Zealand to work on the South Island goldfields. Although the first Chinese migrants had been invited by the Otago Provincial government they quickly became the target of hostility from white settlers and laws were enacted specifically to discourage them from coming to New Zealand.[8]
Naming and usage
Although the island has been known as the South Island for many years, the New Zealand Geographic Board has found that, along with the North Island, it has no official name. The board intends to make South Island the island's official name, along with an alternative Māori name. Although several Māori names have been used, Maori Language Commissioner Erima Henare sees Te Wai Pounamu as the most likely choice.[9] This Māori name for the South Island, meaning "The Water(s) of Greenstone", possibly evolved from Te Wāhi Pounamu which means "The Place Of Greenstone". The island is also known as Te Waka a Māui which means "Māui's Canoe". In Māori legend, the South Island existed first, as the boat of Maui, while the North Island was the fish that he caught.
In the 19th century, some maps named the South Island as Middle Island or New Munster, and the name South Island or New Leinster was used for today's Stewart Island/Rakiura. In 1907 the Minister for Lands gave instructions to the Land and Survey Department that the name Middle Island was not to be used in future. "South Island will be adhered to in all cases".[10]
'The South Island'
The South Island takes the definite article when used as a noun, whereas maps, headings or tables and adjectival expressions use South Island, similar to the United Kingdom.
Government and politics


The South Island has no separately represented country subdivision and is guaranteed 16 of the 69 electorates in the New Zealand House of Representatives. A two-tier structure constituted under the Local Government Act 2002 gives the South Island seven regional councils for the administration of regional environmental and transport matters and 25 territorial authorities that administer roads, sewerage, building consents, and other local matters. Four of the territorial councils (one city and three districts) also perform the functions of a regional council and are known as unitary authorities.
When New Zealand was separated from the colony of New South Wales in 1841 and established as a Crown colony in its own right, the Royal Charter effecting this provided that "the principal Islands, heretofore known as, or commonly called, the 'Northern Island', the 'Middle Island', and 'Stewart's Island', shall henceforward be designated and known respectively as 'New Ulster', 'New Munster', and 'New Leinster'".
These divisions were at first of geographical significance only, not used as a basis for the government of the colony, which was centralised in Auckland. New Munster consisted of the South Island and the southern portion of the North Island, up to the mouth of the Patea River. The name New Munster was given by the Governor of New Zealand, Captain William Hobson, in honour of Munster, the Irish province in which he was born.
The situation was altered in 1846 when the New Zealand Constitution Act 1846.[11] divided the colony into two provinces: New Ulster Province (the North Island), and New Munster Province (the South Island and Stewart Island). Each province had a Governor and Legislative and Executive Council, in addition to the Governor-in-Chief and Legislative and Executive Council for the whole colony. However, the 1846 Constitution Act was later suspended, and only the Provincial government provisions were implemented. Early in 1848 Edward John Eyre was appointed Lieutenant-Governor of New Munster. In 1851 the Provincial Legislative Councils were permitted to be partially elective.
The Provincial Council of New Munster had only one legislative session, in 1849, before it succumbed to the virulent attacks of settlers from Wellington. Governor Sir George Grey, sensible to the pressures, inspired an ordinance of the General Legislative Council under which new Legislative Councils would be established in each province with two-thirds of their members elected on a generous franchise. Grey implemented the ordinance with such deliberation that neither Council met before advice was received that the United Kingdom Parliament had passed the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852.
This act dissolved these provinces in 1853, after only seven years' existence, and New Munster was divided into the provinces of Canterbury, Nelson, and Otago. Each province had its own legislature known as a Provincial Council that elected its own Speaker and Superintendent.
Secession movements have surfaced several times in the South Island. A Premier of New Zealand, Sir Julius Vogel, was amongst the first people to make this call, which was voted on by the Parliament of New Zealand as early as 1865. The desire for the South Island to form a separate colony was one of the main factors in moving the capital of New Zealand from Auckland to Wellington that year.
Several South Island nationalist groups have emerged over recent years including the South Island Party with a pro-South agenda, fielded candidates in the 1999 General Election and a new South Island Party which was formed before the 2008 General Election. Today, several internet based groups advocate their support for greater self determination.[12]
Administrative divisions
Local government regions
There are seven local government regions covering the South Island and all its adjacent islands and territorial waters. Four are governed by an elected regional council, while three are governed by territorial authorities (the second tier of local government) which also perform the functions of a regional council and thus are known as unitary authorities. There is one exception to this, Nelson City, is governed by an individual Territorial authority to its region (Tasman Region). The Chatham Islands Council is often counted by many as a unitary authority, but it is officially recognised as a part of the region of Canterbury.
|
|
Territorial authorities
There are 25 territorial authorities within the South Island: 4 city councils, 20 district councils and the Chatham Islands Council. Four territorial authorities (Nelson City Council, Tasman and Marlborough District Councils and the Chatham Islands Council) also perform the functions of a regional council and thus are known as unitary authorities.
|
|
Political parties
This is a list of Political parties, past and present, who have their headquarters in the South Island.
- Aotearoa Legalise Cannabis Party
- Imperial British Conservative Party
- National Democrats Party
- New Zealand Democratic Party
- New Zealand Progressive Party
- South Island Party
- South Island Party (2008)
Law enforcement
Police


The New Zealand Police is the primary law enforcement agency of New Zealand including the South Island. Three decentralised Police Districts cover the entire South Island with each being commanded by a Superintendent and having a central station from which subsidiary and suburban stations are managed.[13] The Christchurch Police Communications Centre handles all emergency and general calls within the South Island.
The Tasman Police District covers 70,000 kilometres of territory, encompassing the northern and most of the western portion of the South Island. The West Coast alone spans the distance between Wellington and Auckland. There are 22 police stations in the Tasman District, with 6 being sole-charge - or one-person - stations. The Tasman Police District has a total of 302 sworn police officers and 57 civilian or nonsworn staff. Organisationally, the district has its headquarters in Nelson and has three distinct Areas each headed by an Inspector as its commander. The areas are Nelson Bays, West Coast and Marlborough.
The Canterbury Police District is based in Christchurch the largest city in the South Island and covers an area extending from the Conway River, (just south of Kaikoura), to the Waitaki River, south of Timaru.
The Southern Police District with its headquarters in Dunedin spans from Oamaru in the North through to Stewart Island in the far South covers the largest geographical area of any of the 12 police districts in New Zealand.
Correctional facilities
Correctional facilities in the South Island are operated by the Department of Corrections as part of the South Island Prison Region. Christchurch Prison, also known as Paparua, is located in Templeton a satellite town of Christchurch. It accommodates up to 780 minimum, medium and high security male prisoners. It was built in 1925, and also includes a youth unit, a self-care unit and the Paparua Remand Centre (PRC), built in 1999 to replace the old Addington Prison. Christchurch Women's Prison, also located in Templeton, is a facility for women of all security classifications. It has the only maximum/medium security accommodation for women prisoners in New Zealand. It can accommodate up to 98 prisoners.
Rolleston prison is located in Rolleston, another satellite town of Christchurch. It accommodates around 320 male prisoners of minimum to low-medium security classifications and includes Kia Marama a sixty-bed unit that provides an intensive 9 month treatment programme for male child sex offenders. Invercargill Prison, in Invercargill, accommodates up to 172 minimum to low-medium security prisoners. Otago Corrections Facility is located near Milton and houses up to 335 minimum to high-medium security male prisoners.
Customs Service
The New Zealand Customs Service whose role is to provide border control and protect the community from potential risks arising from international trade and travel, as well as collecting duties and taxes on imports to the country has offices at Christchurch International Airport, Dunedin, Invercargill, Lyttelton and Nelson.[14]
People
Population
Compared to the more populated and multi-ethnic North Island, the South Island has a smaller, more homogeneous resident population of 1,038,300 (June 2010 estimate).[15] At the 2001 Census, over 91 percent of people in the South Island said they belong to the European ethnic group, compared with 80.1 percent for all of New Zealand.[16] According to the Statistics New Zealand Subnational Population Projections: 2006–2031; the South Island's population will increase by an average of 0.6 percent a year to 1,047,100 in 2011, 1,080,900 in 2016, 1,107,900 in 2021, 1,130,900 in 2026 and 1,149,400 in 2031.[17]
Economy


The South Island economy is strongly focused on tourism and primary industries like agriculture. The other main industry groups are manufacturing, mining, construction, energy supply, education, health and community services.
Substantial electricity generation (both existing and remaining potential) is located on the South Island, while the main demand (which is continuing to grow) is in the northern North Island, particularly the Auckland Region. The South Island has three large hydroelectric schemes: Waitaki, Clutha, and Manapouri. The Waitaki River is the largest hydroelectric scheme, consisting of nine powerhouses commissioned between 1936 and 1985, and generating approximately 7600 GWh annually, around 18% of New Zealand's electricity generation[18] and more than 30% of all its hydroelectricity.[19] The Clutha River has two major stations generating electricity: Clyde Dam (432 MW, commissioned 1992) and Roxburgh Dam (360 MW, commissioned 1962). Manapouri Power Station is an isolated station located in Southland, generating 730 MW of electricity and producing 4800 GWh annually - the largest single hydroelectric power station in the country.
The HVDC Inter-Island (HVDC) system links the North and South Island electricity grids together. The line connects to the South Island 220 kV grid at Benmore Dam in Southern Canterbury, and travels via pylons for 535 kilometres (332 mi) to Fighting Bay in Marlborough. From here, it crosses the Cook Strait via undersea cables for 40 km to Oteranga Bay, west of Wellington. At Oteranga Bay, the HVDC line converts back to pylons to cover the last 35 km, with the line terminating and connecting to the North Island's 220 kV grid at Haywards in Lower Hutt. The main reason for a HVDC connection between the two islands is due to New Zealand's geography and demographics. The South Island generates 45% of New Zealand's electricity supply, however 75% of New Zealand's population lives in the North Island. HVDC was chosen to allow reactive power to travel between the two islands, northwards to supply the North Island's high electricity demands, and southwards to supply the South Island during years of low hydro levels.
Offshore oil and gas is likely to become an increasing important part of the South Island economy into the future. Origin Energy has formed a joint venture with Anadarko Petroleum, the second-largest independent US natural gas producer to begin drilling for oil in the Canterbury Basin off the coast of Dunedin. The 390 km2, Carrack/Caravel prospect has the potential to deliver more than the equivalent of 500 million barrels of oil and gas. Market analyst, Greg Easton from Craigs Investment Partners commented that such a substantial find it could well turn Dunedin from the Edinburgh of the south to the Aberdeen of the south.[20]
The Great South Basin off the coast of Southland at over 500,000 km2 (covering an area 1.5 times New Zealand’s land mass) is one of New Zealand’s largest undeveloped offshore petroleum basins with prospects for both oil and gas. In July, 2007 the New Zealand Government awarded oil and gas exploration permits for four areas of the Great South Basin, situated in the volatile waters off the Southern Coast of New Zealand. The three successful permit holders are:[21]
- a consortium led by ExxonMobil New Zealand (Exploration) Limited (USA) which includes local company Todd Exploration Limited (New Zealand);
- a consortium led by OMV New Zealand Limited (Austria) which includes PTTEP Offshore Investment Company Ltd (Thailand), Mitsui Exploration and Production Australia Pty Ltd (Japan); and
- Greymouth Petroleum Limited (New Zealand)
The sub-national GDP of the South Island was estimated at US$27.8 billion in 2003, 21% of New Zealand's national GDP.[22]
Stock exchanges
Due to the gold rushes of the 1860s, the South Island had regional stock exchanges in Christchurch, Dunedin and Invercargill – all of which were affiliated in the Stock Exchange Association of New Zealand. However, in 1974 these regional exchanges were amalgamated to form one national stock exchange, the New Zealand Stock Exchange (NZSE). On 30 May 2003, New Zealand Stock Exchange Limited formally changed its name to New Zealand Exchange Limited, trading as NZX.
Today, the Deloitte South Island Index[23] is compiled quarterly from publicly available information provided by NZX, Unlisted and Bloomberg. It is a summary of the movements in market capitalisation of each South Island based listed company. A company is included in the Index where either its registered office and/or a substantial portion of its operations are focused on the South Island.
Trade unions
There are several South Island based trade union organisations. They are:
- Furniture, Manufacturing & Associated Workers Union
- New Zealand Building Trades Union
- New Zealand Meat & Related Trades Workers Union
- Southern Amalgamated Workers' Union
Tourism

Tourism is a huge export earner for the South Island. Popular tourist activities in include sightseeing, adventure tourism, tramping (hiking) and camping. Numerous walking and hiking paths, some of which, like the Milford Track, have huge international recognition.
An increase in direct international flights to Christchurch, Dunedin and Queenstown has boosted the number of overseas tourists.
Fiordland National Park, Abel Tasman National Park, Westland National Park, Aoraki/Mount Cook National Park, Queenstown, Kaikoura and the Marlborough Sounds are regarded as the main tourism destinations in the South Island and amongst the Top 10 destinations in New Zealand.[24]
Ski areas and resorts

This is a list of ski areas and resorts in the South Island.
| Name | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Awakino ski area | Otago | Club Skifield |
| Broken River | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Cardrona Alpine Resort | Otago | |
| Coronet Peak | Otago | |
| Craigieburn Valley | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Fox Peak | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Hanmer Springs Ski Area | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Invincible Snowfields | Otago | Helicopter access only |
| Mount Cheeseman | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Mount Dobson | Canterbury | |
| Mount Hutt | Canterbury | |
| Mount Olympus | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Mount Potts | Canterbury | Heliskiing and snowcatting only |
| Mount Robert | Tasman | Club Skifield |
| Ohau | Canterbury | |
| Porter Heights | Canterbury | |
| Rainbow | Tasman | |
| The Remarkables | Otago | |
| Round Hill | Canterbury | |
| Snow Farm | Otago | cross-country skiing |
| Snow Park | Otago | |
| Tasman Glacier | Canterbury | Heliskiing |
| Temple Basin | Canterbury | Club Skifield |
| Treble Cone | Otago |
Transport
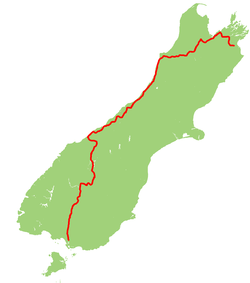
.
Road transport
The South Island has a State Highway network of 4,921 km.
Rail transport

- See also: List of New Zealand railway lines, Rail transport in New Zealand.
The South Island's railway network has two main lines, two secondary lines, and a few branch lines. The Main North Line from Picton to Christchurch and the Main South Line from Lyttelton to Invercargill via Dunedin together comprise the South Island Main Trunk Railway. The secondary Midland Line branches from the Main South Line in Rolleston and passes through the Southern Alps via the Otira Tunnel to the West Coast and its terminus in Greymouth. In Stillwater, it meets the other secondary route, the Stillwater - Westport Line, which now includes the Ngakawau Branch.
A number of other secondary routes are now closed, including the Otago Central Railway, the isolated Nelson Section, and the interdependent Waimea Plains Railway and Kingston Branch. An expansive network of branch lines once existed, especially in Canterbury, Otago, and Southland, but these are now almost completely closed. The branch lines that remain in operation serve ports (Bluff Branch and Port Chalmers Branch), coal mines (Ohai Branch and Rapahoe Branch), and a dairying factory (Hokitika Branch). The first 64 km of the Otago Central Railway remain in operation for tourist trains run by the Taieri Gorge Railway (TGR). The most significant freight is coal from West Coast mines to the port of Lyttelton for export.
Passenger services were once extensive. Commuter trains operated multiple routes around Christchurch and Dunedin, plus a service between Invercargill and Bluff. Due to substantial losses, these were cancelled between the late 1960s and early 1980s. The final services to operate ran between Dunedin and Mosgiel, and they ceased in 1982.[25] Regional passenger trains were once extensive, but are now limited to the TranzCoastal from Christchurch to Picton and the TranzAlpine from Christchurch to Greymouth.
The Southerner between Christchurch and Invercargill, once the flagship of the network, was cancelled on 10 February 2002. Subsequently, the architecturally significant Dunedin Railway Station has been used solely by the TGR's tourist trains, the Taieri Gorge Limited along the Otago Central Railway and the Seasider to Palmerston. Rural passenger services on branch lines were provided by mixed trains and Vulcan/88 seater railcars but the mixeds had largely ceased to exist by the 1950s and the railcars were withdrawn in the mid-1970s.
The South Island saw the final use of steam locomotives in New Zealand. Locomotives belonging to classes long withdrawn elsewhere continued to operate on West Coast branches until the very late 1960s, when they were displaced by DJ class diesels. In comparison to most countries, where steam locomotives were last used on insubstantial rural and industrial operations, the very last services run by steam locomotives were the premier expresses between Christchurch and Invercargill: the South Island Limited until 1970 and the Friday and Sunday night services until 1971. This was due to the carriages being steam-heated. The final steam-hauled service in New Zealand, headed by a member of the JA class, ran on 26 October 1971.[26]
Water transport

The South Island is separated from the North Island by Cook Strait, 24 km wide at its narrowest point, but requiring a 70 km ferry trip to cross.
Ports and harbours
- Container ports: Lyttelton (Christchurch), Port Chalmers (Dunedin)
- Other ports: Nelson, Picton, Westport, Greymouth, Timaru, Bluff.
- Harbours: Akaroa, Otago Harbour, Halfmoon Bay (Stewart Island/Rakiura), Milford Sound.
- Freshwater: Queenstown and Kingston (Lake Wakatipu), Te Anau and Manapouri (Lake Manapouri)
Air transport
Airports



| LOCATION | ICAO | IATA | AIRPORT NAME |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandra | NZLX | ALR | Alexandra Aerodrome |
| Ashburton | NZAS | ASG | Ashburton Aerodrome |
| Balclutha | NZBA | Balclutha Aerodrome | |
| Blenheim | NZWB | BHE | Blenheim Airport (Woodbourne) |
| Chatham Islands | NZCI | CHT | Chatham Islands / Tuuta Airport |
| Christchurch | NZCH | CHC | Christchurch International Airport (long-distance) |
| Cromwell | NZCS | Cromwell Racecourse Aerodrome | |
| Dunedin | NZDN | DUD | Dunedin International Airport (limited) |
| Gore | NZGC | Gore Aerodrome | |
| Greymouth | NZGM | GMN | Greymouth Airport |
| Haast | NZHT | Haast Aerodrome | |
| Hokitika | NZHK | HKK | Hokitika Airport |
| Invercargill | NZNV | IVC | Invercargill Airport |
| Kaikoura | NZKI | KBZ | Kaikoura Aerodrome |
| Lake Pukaki | NZGT | GTN | Glentanner Aerodrome |
| Milford Sound | NZMF | MFN | Milford Sound Airport |
| Mount Cook | NZMC | MON | Mount Cook Aerodrome |
| Motueka | NZMK | MZP | Motueka Aerodrome |
| Nelson | NZNS | NSN | Nelson Airport |
| Oamaru | NZOU | OAM | Oamaru Aerodrome |
| Picton | NZPN | PCN | Picton Aerodrome |
| Queenstown | NZQN | ZQN | Queenstown Airport (limited) |
| Rangiora | NZFF | Forest Field Aerodrome | |
| Stewart Island/Rakiura | NZRC | SZS | Ryans Creek Aerodrome |
| Takaka | NZTK | KTF | Takaka Aerodrome |
| Te Anau / Manapouri | NZMO | TEU | Manapouri Aerodrome |
| Timaru | NZTU | TIU | Richard Pearse Airport |
| Twizel | NZUK | TWZ | Pukaki Aerodrome |
| Wanaka | NZWF | WKA | Wanaka Airport |
| Westport | NZWS | WSZ | Westport Airport |
| Wigram | NZWG | Wigram Aerodrome |
Geography


The South Island, with an area of 151,215 km² (58,093 square miles), is the largest land mass of New Zealand; it contains about one quarter of the New Zealand population and is the world's 12th-largest island. It is divided along its length by the Southern Alps, the highest peak of which is Aoraki/Mount Cook at 3754 metres (12,316 ft). There are eighteen peaks of more than 3000 metres (9800 ft) in the South Island. The east side of the island is home to the Canterbury Plains while the West Coast is famous for its rough coastlines, very high proportion of native bush, and Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers. The dramatic landscape of the South Island has made it a popular location for the production of several films, including the Lord of the Rings trilogy and the The Chronicles of Narnia: The Lion, The Witch, and the Wardrobe.
Climate
The climate in the South Island is mostly temperate. The Mean temperature for the South Island is 8 °C (46 °F).[27] January and February are the warmest months while July is the coldest. Historical maxima and minima are 42.4 °C (108.3 °F) in Rangiora, Canterbury and −21.6 °C (−6.9 °F) in Ophir, Otago.[28]
Conditions vary sharply across the regions from extremely wet on the West Coast to semi-arid in the Mackenzie Basin of inland Canterbury. Most areas have between 600 and 1600 mm of rainfall with the most rain along the West Coast and the least rain on the East Coast, predominantly on the Canterbury Plains. Christchurch is the driest city receiving about 640 mm (25 in) of rain per year. The southern and south-western parts of South Island have a cooler and cloudier climate, with around 1400–1600 hours of sunshine annually; the northern and north-eastern parts of the South Island are the sunniest areas and receive approximately 2400–2500 hours.[29]
Protected areas of the South Island
Forest Parks

There are six Forest Parks in the South Island which are on public land administered by the Department of Conservation.
- Catlins Forest Park
- Situated in the Southland region.
- Craigieburn Forest Park
- Situated in the Canterbury region, its boundaries lie in part alongside State Highway 73 and is adjacent to the eastern flanks of the Southern Alps. The Broken River Ski Area and the Craigieburn Valley Ski Area lie within its borders. The New Zealand Forest Service had used the area as an experimental forestry area and there is now an environmental issue with the spread of wilding conifers.
- Hanmer Forest Park
- Situated in the Canterbury region.
- Lake Sumner Forest Park
- Situated in the Canterbury region.
- Mount Richmond Forest Park
- Situated in the Marlborough region.
- Victoria Forest Park
- Situated in the West Coast region.
National parks


The South Island has ten national parks established under the National Parks Act 1980 and which are administered by the Department of Conservation.
From north to south, the National Parks are:
- Kahurangi National Park
- (4,520 km², established 1996) Situated in the north-west of the South Island, Kahurangi comprises spectacular and remote country and includes the Heaphy Track. It has ancient landforms and unique flora and fauna. It is New Zealand's second largest national park.
- Abel Tasman National Park
- (225 km², established 1942) Has numerous tidal inlets and beaches of golden sand along the shores of Tasman Bay. It is New Zealand's smallest national park.
- Nelson Lakes National Park
- (1,018 km², established 1956) A rugged, mountainous area in Nelson Region. It extends southwards from the forested shores of Lake Rotoiti and Rotoroa to the Lewis Pass National Reserve.
- Paparoa National Park
- (306 km², established 1987) On the West Coast of the South Island between Westport and Greymouth. It includes the celebrated Pancake Rocks at Punakaiki.
- Arthur's Pass National Park
- (1,144 km², established 1929) A rugged and mountainous area straddling the main divide of the Southern Alps.
- Westland Tai Poutini National Park
- (1,175 km², established 1960) Extends from the highest peaks of the Southern Alps to a wild remote coastline. Included in the park are glaciers, scenic lakes and dense rainforest, plus remains of old gold mining towns along the coast.
- Aoraki/Mount Cook National Park
- (707 km², established 1953) An alpine park, containing New Zealand's highest mountain, Aoraki/Mount Cook (3,754 m) and its longest glacier, Tasman Glacier (29 km). A focus for mountaineering, ski touring and scenic flights, the park is an area of outstanding natural beauty. Together, the Mount Cook and Westland National Parks have been declared a World Heritage Site.
- Mount Aspiring National Park
- (3,555 km², established 1964) A complex of impressively glaciated mountain scenery centred on Mount Aspiring/Tititea (3,036 m), New Zealand's highest peak outside of the main divide.
- Fiordland National Park
- (12,519 km², established 1952) The largest national park in New Zealand and one of the largest in the world. The grandeur of its scenery, with its deep fiords, its lakes of glacial origin, its mountains and waterfalls, has earned it international recognition as a world heritage area.
- Rakiura National Park
- (1,500 km², established 2002) On Stewart Island/Rakiura.
Other Native Reserves and Parks
- Hakatere Conservation Park [30]
Birds

There are several bird species which are endemic to the South Island. They include the Kea, Great Spotted Kiwi, Okarito Brown Kiwi, South Island Kōkako, South Island Pied Oystercatcher, Malherbe's Parakeet, King Shag, Takahe, Black-fronted Tern, New Zealand Robin, Rock Wren, Wrybill, Yellowhead
Unfortunately many South Island bird species are now extinct, mainly due to predation by cats and rats introduced by humans. Extinct species include the South Island Goose, South Island Giant Moa and South Island Piopio.
Natural geographic features
Fjords

The South Island has 15 named maritime fiords which are all located in the southwest of the island in a mountainous area known as Fiordland. The spelling 'fiord' is used in New Zealand, although all the maritime fjords use the word Sound in their name instead.
A number of lakes in the Fiordland and Otago regions also fill glacial valleys. Lake Te Anau has three western arms which are fjords (and are named so). Lake McKerrow to the north of Milford Sound is a fjord with a silted-up mouth. Lake Wakatipu fills a large glacial valley, as do lakes Hakapoua, Poteriteri, Monowai and Hauroko in the far south of Fiordland. Lake Manapouri has fjords as its West, North and South arms.
The Marlborough Sounds, are a series of deep indentations in the coastline at the northern tip of the South Island, are in fact rias, drowned river valleys.
Glaciers
Most of New Zealand's glaciers are in the South Island. They are generally found in the Southern Alps near the Main Divide.
An inventory of South Island glaciers during the 1980s indicated there were about 3,155 glaciers with an area of at least one hectare (2.5 acres).[31] Approximately one sixth of these glaciers covered more than 10 hectares. These include the Fox and Franz Josef glaciers on the West Coast, and the Tasman, Hooker, Mueller and Murchison glaciers in the east.
Lakes

There are some 3,820 lakes in New Zealand with a surface area larger than one hectare. Much of the higher country in the South Island was covered by ice during the glacial periods of the last two million years. Advancing glaciers eroded large steep-sided valleys, and often carried piles of moraine (rocks and soil) that acted as natural dams. When the glaciers retreated, they left basins that are now filled by lakes. The level of most glacial lakes in the upper parts of the Waitaki and Clutha rivers are controlled for electricity generation. Hydroelectric reservoirs are common in South Canterbury and Central Otago, the largest of which is Lake Benmore, on the Waitaki River.
The South Island has 8 of New Zealand's 10 biggest lakes. They were formed by glaciers and include Lake Wakatipu, Lake Tekapo and Lake Manapouri. The deepest (462 metres) is Lake Hauroko, in western Southland. It is the 16th deepest lake in the world. Millions of years ago, Central Otago had a huge lake – Lake Manuherikia. It was slowly filled in with mud, and fossils of fish and crocodiles have been found there.
Volcanoes

There are 4 extinct volcanoes in the South Island, all of which are located on the east coast.
Banks Peninsula forms the most prominent of these volcanic features. Geologically, the peninsula comprises the eroded remnants of two large shield volcanoes (Lyttelton formed first, then Akaroa). These formed due to intraplate volcanism between approximately eleven and eight million years ago (Miocene) on a continental crust. The peninsula formed as offshore islands, with the volcanoes reaching to about 1,500 m above sea level. Two dominant craters formed Lyttelton and Akaroa Harbours.
The Canterbury Plains formed from the erosion of the Southern Alps (an extensive and high mountain range caused by the meeting of the Indo-Australian and Pacific tectonic plates) and from the alluvial fans created by large braided rivers. These plains reach their widest point where they meet the hilly sub-region of Banks Peninsula. A layer of loess, a rather unstable fine silt deposited by the foehn winds which bluster across the plains, covers the northern and western flanks of the peninsula. The portion of crater rim lying between Lyttelton Harbour and Christchurch city forms the Port Hills.
The Otago Harbour was formed from the drowned remnants of a giant shield volcano, centred close to what is now the town of Port Chalmers. The remains of this violent origin can be seen in the basalt of the surrounding hills. The last eruptive phase ended some ten million years ago, leaving the prominent peak of Mount Cargill.
Timaru was constructed on rolling hills created from the lava flows of the extinct Mount Horrible, which last erupted many thousands of years ago.
Te Wāhipounamu World Heritage site
Te Wāhipounamu (Māori for "the place of greenstone") is a World Heritage site in the south west corner of the South Island.[32]
Inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1990 it covers 26,000 km² and incorporates the Aoraki/Mount Cook, the Fiordland, the Mount Aspiring and the Westland National Parks.
It is thought to contain some of the best modern representations of the original flora and fauna present in Gondwanaland, one of the reasons for listing as a World Heritage site.
Education

The South Island has several tertiary level institutions:
- Aoraki Polytechnic
- Christchurch Polytechnic Institute of Technology
- Lincoln University
- Nelson Marlborough Institute of Technology
- Otago Polytechnic
- Southern Institute of Technology
- Tai Poutini Polytechnic
- Telford Rural Polytechnic
- University of Canterbury
- University of Otago
Healthcare


Healthcare in the South Island is provided by six District Health Boards (DHBs). Organized around geographical areas of varying population sizes, they are not coterminous with the Local Government Regions.
| Name | Area covered | Population[33] |
|---|---|---|
| Canterbury District Health Board | Ashburton District, Christchurch City, Hurunui District, Kaikoura District, Selwyn District, Waimakariri District | 491,000 |
| Nelson Marlborough District Health Board | Marlborough District, Nelson City, Tasman District, | 135,000 |
| Otago District Health Board | Central Otago District, Clutha District, Dunedin City, Queenstown Lakes District, Waitaki District | 185,000 |
| South Canterbury District Health Board | Mackenzie District, Timaru District, Waimate District | 55,000 |
| Southland District Health Board | Gore District, Invercargill City, Southland District | 110,000 |
| West Coast District Health Board | Buller District, Grey District, Westland District | 32,000 |
Emergency medical services
There are several air ambulance and rescue helicopter services operating throughout the South Island.[34]
- The Lake Districts Air Rescue Trust operates two AS350BA Squirrel's and a AS355 Squirrel from Queenstown Airport.
- The New Zealand Flying Doctor Service operates a Cessna 421 Golden Eagle and a Cessna Conquest C441 from Christchurch International Airport.[35]
- The Otago Rescue Helicopter Trust operates a MBB/Kawasaki BK 117 from Taieri Aerodrome near Mosgiel.
- The Solid Energy Rescue Helicopter Trust operates a AS350BA Squirrel from Greymouth.
- The Summit Rescue Helicopter Trust operates a AS350BA Squirrel from Nelson Airport.
- The Westpac Rescue Helicopter Trust operates a MBB/Kawasaki BK 117 and a AS350BA Squirrel from Christchurch International Airport.
Culture
Art

The South Island has contributed to the Arts in New Zealand and internationally through highly regarded artists such as Nigel Brown, Frances Hodgkins, Colin McCahon, Shona McFarlane, Peter McIntyre Grahame Sydney and Geoff Williams.
The University of Canterbury School of Fine Arts was founded in 1950.
South Island Art Galleries include:
- Centre of Contemporary Art
- Christchurch Arts Centre
- Dunedin Public Art Gallery
Language
Parts of the South Island principally Southland and Otago are famous for its people speaking what is often referred to as the "Southland burr", a semi-rhotic, Scottish-influenced dialect of the English language.
Media
Newspapers


The South Island has 11 daily newspapers and an increasing number of weekly community newspapers. Newspapers are still an important form of communication for many people particularly those living in isolated rural communities.
| Newspaper | Frequency | Owner | Founded | Headquarters | Circulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ashburton's The Courier | Weekly | Allied Press | 1985 | Ashburton | 12,500 |
| Ashburton Guardian | Daily | Bruce Bell | 1879 | Ashburton | 5,554 |
| The Courier | Weekly | Allied Press | Timaru | 24,500 | |
| Courier Country | Allied Press | Timaru | 13,000 | ||
| The Ensign | Twice Weekly | Allied Press | 1878 | Gore | 11,500 |
| The Greymouth Star | Daily | Allied Press | 1866 | Greymouth | |
| Hurunui News | Bi-Weekly | Allied Press | Amberley | ||
| The Marlborough Express | Daily | Fairfax Media | Blenheim | ||
| Motueka Golden Bay News | Weekly | Nelson | 20,000 | ||
| Nelson City Leader | Weekly | Nelson | 49,000 | ||
| The Nelson Mail | Daily | Fairfax Media | 1866 | Nelson | |
| The News | Weekly | Allied Press | 1948 | Alexandra | 17,600 |
| Oamaru Mail | Daily | APN News & Media | 1876 | Oamaru | 10,000 |
| Otago Daily Times | Daily | Allied Press | 1861 | Dunedin | 43,000 |
| The Press | Daily | Fairfax Media | 1861 | Christchurch | 90,000 |
| Queenstown Times | Daily | Allied Press | Queenstown | ||
| Richmond Waimea Leader | Weekly | Nelson | 49,000 | ||
| Southern Rural Life | Fortnightly | Allied Press | Dunedin | 20,000 | |
| Southland Express | Weekly | Allied Press | Invercargill | ||
| Southland Times | Daily | Fairfax Media | 1862 | Invercargill | 29,384 |
| The Star | Weekly | Allied Press | 1979 | Dunedin | 43,500 |
| The Timaru Herald | Daily | Fairfax Media | 1864 | Invercargill | 14,500 |
| The West Coast Messenger | Weekly | Allied Press | 2003 | Greymouth | |
| West Coast Times | Daily | Allied Press | 1865 | Hokitika |
Television
The South Island has 7 regional stations (either non-commercial public service or privately owned) that broadcast only in one region or city. These stations mainly broadcast free to air on UHF frequencies, however some are carried on subscription TV. Content ranges from local news, access broadcasts, satellite sourced news, tourist information and Christian programming to music videos.
| Name | Service region | Availability | Notes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analogue terrestrial | Sky Digital satellite | Freeview satellite | Freeview|HD terrestrial | TelstraClear cable | |||
| Mainland Television | Nelson | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| Shine TV | Christchurch | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Christian programming |
| CTV Canterbury Television | Christchurch | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | |
| Visitor TV | Christchurch | Yes | No | No | No | No | Tourist information |
| 45 South TV | Timaru / Oamaru | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| Channel 9 | Dunedin | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| CUE | Southland | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Formerly Mercury Television and later Southland TV. Mainly distance learning, local news and sport |
Radio Stations
| Name | Logo | Place | Frequency (MHz) | Owner | Website | Webcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4ZA |
 |
Southland |
|
|
||
| Foveaux FM |
 |
Southland |
|
|
||
| Fresh FM |
|
Nelson/Tasman |
Tasman 104.8FM Takaka 95.2FM Blenheim 89.2FM |
|
|
|
| Hokonui Gold |
 |
Southland |
|
|
|
|
| Port FM | South Canterbury |
|
||||
| Pulzar FM | Christchurch |
|
|
|
Nelson stations
Current stations
- Impact 100
- Mainland FM
- Radio Robot
Previous stations
- Cadbury Moro FM
- Fifeshire FM - Rebranded as More FM
- Radio Nelson - Rebranded as Classic Hits 89.8 & 90.4FM
- The Planet 97FM - Replaced with ZM
West Coast stations
Current stations
- Coast FM - no connection to the Coast Radio Network, operated by The Radio Network.
- Classic Hits FM - see below.
Previous stations
- Radio Scenicland and later Scenicland FM - Rebranded as Classic Hits Scenicland FM.
Canterbury stations
Current stations
- 91ZM - Operates local daytime show all other shows from the ZM network. Originally local until 2001.
- Newstalk ZB
- Plains 96.9FM
- Radio Ferrymead
- RDU-FM
Previous stations
- 3ZB - Rebranded as Newstalk ZB
- 3ZE (Ashburton) - Rebranded as Classic Hits 92.5 ZEFM
- Channel Z - Operated local Channel Z station until 2001 when station was replaced with Auckland based network product.
- Fox FM (Ashburton) - Rebranded as Port FM
- 99 Life FM - Original Life FM station
- B98 FM - Rebranded as Classic Hits B98 and later Classic Hits 97.7
- Lite FM - Rebranded as The Breeze
- Radio Avon and later C93FM
- Radio Caroline (Timaru) - Rebranded as Classic Hits 99FM
- Blush 96.1 - Christchurch NZBS "Live Sexy"
Dunedin and East Otago stations
Current stations
- Big River Radio (Balclutha)
- Country Radio 88.7
- Ear107
- GoldRush1440 (Lawrence)
- Hills AM
- Radio Clutha (Balclutha)
- Radio Dunedin
- Radio One
- RushFM (Lawrence)
Previous stations
- 4XO - Rebranded as More FM
- 4ZB and later ZBFM - Rebranded as Classic Hits 89FM
- 93Rox
- Radio Waitaki (Oamaru) - Rebranded as Classic Hits Radio Waitaki
- Whitestone FM (Oamaru) - Rebranded as Port FM
Queenstown and Central Otago stations
Current Stations
- 96.7 Blue Skies FM (Alexandra)
- Burn 729AM (Ranfurly)
- The Studio FM (Queenstown)
- Radio Wanaka (Wanaka)
Previous stations
- Radio Central (Alexandra) - Rebranded as More FM
- Resort Radio (Queenstown) - Rebranded as More FM
- Q92FM (Queenstown) - Rebranded as Q92 The Breeze
Southland stations
Current stations
- Country Radio 88.4
- Radio Southland 96.4
Previous stations
- eFM - Southern Institute of Technology student radio station that operated in 2001.
Museums
- Canterbury Museum
- Ferrymead Heritage Park
- Nelson Provincial Museum [3]
- Otago Museum
- Otago Settlers Museum
- Royal New Zealand Air Force Museum
- Southland museum and art gallery
- World of Wearable Art
Religion

Anglicanism is strongest in Canterbury (the city of Christchurch having been founded as an Anglican settlement).
Catholicism is still has a noticeably strong presence on the West Coast, and in Kaikoura. The territorial authorities with the highest proportion of Catholics are Kaikoura (where they are 18.4% of the total population), Westland (18.3%), and Grey (17.8%).
Presbyterianism is strong in the lower South Island — the city of Dunedin was founded as a Presbyterian settlement, and many of the early settlers in the region were Scottish Presbyterians. The territorial authorities with the highest proportion of Presbyterians are Gore (where they are 30.9% of the total population), Clutha District (30.7%), and Southland (29.8%).
The first Muslims in New Zealand were Chinese golddiggers working in the Dunstan gold fields of Otago in the 1860s. Dunedin's Al-Huda mosque is reputedly the world's southernmost, and is further from Mecca than any other mosque in the Southern Hemisphere.
Sport
A number of national or international sporting teams and events are based in the South Island, including:
- Basketball: Canterbury Rams, Nelson Giants, Otago Nuggets
- Cricket: Central Stags, Canterbury Wizards, Otago Volts
- Football (soccer): Canterbury United, Otago United.
- Ice hockey: Canterbury Red Devils, Dunedin Thunder, Southern Stampede.
- Netball: Canterbury Tactix, Southern Steel.
- Rugby league: Canterbury Bulls
- Rugby union: Crusaders, Highlanders (Super 14), Canterbury, Otago, Southland Stags, Tasman Makos (ITM Cup), Buller, South Canterbury, Mid Canterbury, North Otago, West Coast (Heartland Championship)
The South Island occasionally hosts matches for North Island based teams who compete in Trans-Tasman sporting competition. Christchurch has hosted home fixtures for the Auckland-based New Zealand Breakers (basketball) and now-defunct Football Kingz FC (football), as well as fixtures for the Wellington-based Wellington Phoenix FC (football). Christchurch has also rugby league matches between the Auckland-based New Zealand Warriors and the Sydney-based Wests Tigers as the result of the Tigers relocating some of their home matches to Lancaster Park.
Christchurch also hosted the 1974 Commonwealth Games.
See also
- Flag concepts for the South Island
- List of twin towns and sister cities in the South Island
- Military of the South Island
- New Munster
- South Island Independence
- South Island nationalism
References
- ↑ King, Michael (2003). The Penguin History of New Zealand. Auckland: Penguin Books. pp. 280–281. ISBN 0143018671. http://penguin.co.nz/afa.asp?idWebPage=30233&ID=1788742&Sisbn=858711552.
- ↑ Michael King (2003). The Penguin History of New Zealand. Penguin Books. p. 90. ISBN 0-14-301867-1.
- ↑ Moriori - The impact of new arrivals - Te Ara Encyclopedia of New Zealand
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Tau, Te Maire. "Ngāi Tahu". Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand. http://www.teara.govt.nz/NewZealanders/MaoriNewZealanders/NgaiTahu/en
- ↑ A.H. McLintock (ed), An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand”, 3 vols, Wellington, NZ:R.E. Owen, Government Printer, 1966, vol 3 p. 526.'
- ↑ "The Ngai Tahu Report 1991". http://www.waitangi-tribunal.govt.nz/reports/viewchapter.asp?reportID=D5D84302-EB22-4A52-BE78-16AF39F71D91&chapter=30.
- ↑ Michael King (2003). The Penguin History of New Zealand. Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-301867-1.
- ↑ Manying Ip. 'Chinese', Te Ara—the Encyclopedia of New Zealand, updated 21-Dec-2006, http://www.TeAra.govt.nz/NewZealanders/NewZealandPeoples/Chinese/en
- ↑ Isaac Davison, North and South Islands officially nameless, New Zealand Herald, 22 April 2009. Retrieved 22 April 2009.
- ↑ "The Waitara Harbour Bill". Taranaki Herald. 30 July 1907. p. 4. http://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/cgi-bin/paperspast?a=d&d=TH19070730.2.22.
- ↑ [1] Text of the 1846 Constitution from the [London Gazette]
- ↑ Written submission in support of application for broadcasting funding, Richard Prosser, 18 April 2008
- ↑ New Zealand Police Districts
- ↑ Customs Service Offices - New Zealand
- ↑ "Subnational population estimates at 30 June 2010 (boundaries at 1 November 2010)". Statistics New Zealand. 26 October 2010. http://www.stats.govt.nz/~/media/Statistics/Methods%20and%20Services/Tables/Subnational%20population%20estimates/subnational-pop-estimate-jun2001-2010.ashx. Retrieved 26 October 2010.
- ↑ Statistics New Zealand
- ↑ http://www.stats.govt.nz/~/media/Statistics/Browse%20for%20stats/SubnationalPopulationProjections/HOTP2031/SPP-06-31-tables.ashx
- ↑ "MED Energy Sector Information: Waitaki River". MED. http://www.med.govt.nz/templates/MultipageDocumentPage____10581.aspx. Retrieved 2008-12-24.
- ↑ "Home > Projects > Aviemore Dam". URS Corp.. http://www.urscorp.com/Projects/projView.php?s=354. Retrieved 2009-01-15.
- ↑ Published: 1:30PM Thursday February 25, 2010 (2010-02-25). "Origin in joint exploration venture in Canterbury Basin | BUSINESS News". Tvnz.co.nz. http://tvnz.co.nz/business-news/origin-begin-exploration-off-south-island-3382251. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ↑ "Southland Energy Consortium". Energy.southlandnz.com. http://energy.southlandnz.com/BusinessinSouthland/OilGasMinerals/GreatSouthBasin.aspx. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ↑ "Regional Gross Domestic Product". Statistics New Zealand. 2007. http://www.stats.govt.nz/reports/analytical-reports/regional-gross-domestic-product.aspx. Retrieved 18 February 2010.
- ↑ "South Island Index". Deloitte.com. 2006-12-31. http://www.deloitte.com/dtt/section_node/0,1042,sid%253D193345,00.html. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ↑ Top Ten Tourist Attractions in New Zealand
- ↑ Tony Hurst, Farewell to Steam: Four Decades of Change on New Zealand Railways (Auckland: HarperCollins, 1995), 96.
- ↑ David Leitch, Steam, Steel and Splendour (Auckland: HarperCollins, 1994), 89.
- ↑ From NIWA Science climate overview.
- ↑ "Summary of New Zealand climate extremes". National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research. 2004. http://www.niwascience.co.nz/edu/resources/climate/extreme/. Retrieved 2008-02-17.
- ↑ "Mean monthly sunshine hours" (XLS). National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research. http://www.niwascience.co.nz/__data/assets/file/0006/44655/sunshine.xls.
- ↑ Hakatere Conservation Park, Department of Conservation website. Retrieved 21 January 2008.
- ↑ Chinn, Trevor J.H., (1988), Glaciers of New Zealand, in Satellite image atlas of glaciers of the world, U.S. Geological Survey professional paper; 1386, ISBN 0-607-71457-3.
- ↑ "UNESCO World Heritage official website listing". http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/551.
- ↑ "What are the populations served by DHBs? - FAQs about DHBs - Ministry of Health". http://www.moh.govt.nz/moh.nsf/indexmh/dhb-faq#7. Retrieved 2009-05-11.. Population based on Statistics New Zealand population projections in September 2007.
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ New Zealand Flying Doctor Service
External links
- South Island
- South Island Road Map
- South Island travel guide from Wikitravel
|
||||||||||||||
